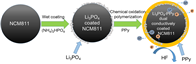
 Figure 1. Schematic of dual conductively coatingof LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 cathode material with Li3PO4 and PPy. |
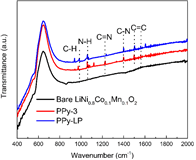 Figure 2. FT-IR spectra of bare LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2, PPy-3 and PPy-LP samples. |
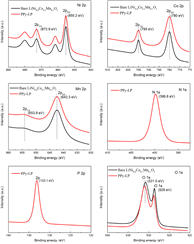 Figure 3. XPS patterns of bare LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 and PPy-LP samples. |
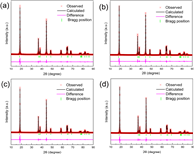 Figure 4. XRD patterns and Rietveld refinement results for the (a) bare LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2, (b) LP-2, (c) PPy-3, and (d) PPy-LP samples. |
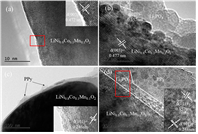 Figure 5. TEM images of (a) bare LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2, (b) LP-2, (c) PPy-3, and (d) PPy-LP samples. |
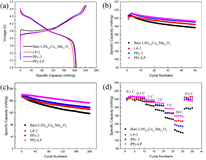 Figure 6. (a) The initial charge and discharge curves, (b) cycling properties at 0.1 C, (c) cycling properties at 1 C, and (d) rate properties of bare LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2, LP-2, PPy-3, and PPy-LP samples between 2.8 and 4.5 V at 25 °C. |
 Figure 7. SEM images of cross section for the (a) bare LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2, (b) LP-2, (c) PPy-3, and (d) PPy-LP cathode materials after 50 cycles. |
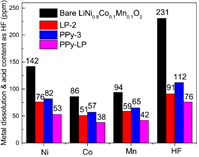 Figure 8. HF titration results and the amount of dissolved transition metal ions in the electrolyte of bare and surface-modified LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 cells after being cycled 50 times. |
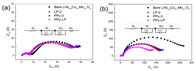 Figure 9. Nyquist plots of bare LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2, LP-2, PPy-3, and PPy-LP samples after (a) 1st and (b) 50th cycles; the inset is the equivalent circuit model. |
- Title : Ni-Rich LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 Oxide Coated by Dual-Conductive Layers as High Performance Cathode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries ( ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 9 (2017) 29732-29743 ) - 본 논문에서는 Ni-rich 층상계 LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2의 성능을 개선하기 위하여 활물질에 Li3PO4와 PPy가 포함된 dual-conductive layers를 코팅하였다. 이온 전도도가 높지만 전자전도도가 낮고 균일한 코팅이 어려운 Li3PO4의 단점을 PPy코팅을 통해 보완하였고 그 결과 bare 및 단일코팅 물질에 비해 수명과 Rate특성이 크게 향상됨을 보여주었다.
- 공침을 통해 [LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1](OH)2를 얻고, Li2CO3와 소성하여 LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 bare물질을 합성하였다. 0.1wt% PVP와 2wt% (NH4)2HPO4를 ethyl alcohol에 넣어 stirring한 후(24h), bare물질을 추가하여 stirring한다. 이후 45℃에서 용매를 증발시킨 후 450℃에서 열처리 하여 Li3PO4를 코팅하였다(LP-2). Liquid pyrrole monomer와 도핑 agent(sodium p-toluenesulfonate)를 ethyl alcohol에 stirring하고, bare물질 또는 LP-2를 추가한 후 stirring한다. 산화제로 FeCl3·6H2O를 천천히 주입하고 polymerization시킨다. 여과 및 세척 후 건조하여 PPy 코팅 층을 얻었다. - FT-IR와 XPS를 통해 Li3PO4와 PPy이 표면에 코팅되었음을 확인하였다. XPS Ni 2p, Co 2p, Mn 2p peak를 통해 표면의 각 이온의 구조적 환경이 변하지 않았으며, XRD pattern에서 코팅 전후 bulk 결정구조가 변하지 않았음을 보여준다. TEM을 통해 각 샘플별로 particle 표면 및 코팅 층을 확인 하였다. - 초기용량은 LP-2에서 일부 감소하지만, PPy-3와 PPy-LP는 bare와 큰 차이가 없었다. 수명은 bare보다 surface-modified샘플들이 더 우수했으며, 특히 dual-coating된 PPy-LP가 retention 95.1%(0.1C,50cycle), 86.5%(1C,200cycle)로 가장 우수했다. Rate특성도 surface-modified샘플이 더 우수했으며, 그 중 PPy-LP가 가장 우수한 결과를 나타냈다. - Cycle시 부반응에 의해 생성되는 HF 및 transition metal의 dissolution은 양극 활물질 구조붕괴 및 용량감소를 초래하는 것으로 알려져 있다. Cross section SEM 이미지에서 bare는 cycle 평가 후 particle에 큰 crack들이 발생하였지만, PPy-LP는 Li3PO4의 HF 형성 억제효과와 신축성있는 PPy코팅의 내부압력 감소효과로 cycle 후에도 particle이 온전히 유지되는 결과를 얻었다. cycle 후 전해액을 분석한 결과 HF 및 TM dissolution이 surface-modified 샘플에서 적게 발생했으며, 특히 PPy-LP에서 가장 적게 발생하였다. - EIS 결과, 초기 저항은 큰 차이가 없지만, cycle 후 Rct 저항이 급격히 증가했다. Bare가 가장 크게 증가한 반면 PPy-LP의 증가 정도가 가장 작았다. 또한 low frequency의 diffusion구간으로 Li+ diffusion coefficient를 계산한 결과 bare는 9.4X10-13, LP-2, PPy-3, PPy-LP는 각각 2.2X10-12, 1.4X10-12, 2.4X10-12 cm2/s로 PPy-LP가 가장 높은 값을 나타냈다. - 결과적으로, Li3PO4와 PPy dual-coating은 Li3PO4을 통한 잔류리튬 감소, Rct저항 감소, Li+ diffusion coefficient 향상 효과와 PPy의 균일하고 신축성있는 코팅 및 부반응 억제 효과 로 인해 우수한 전기화학특성을 얻을 수 있었다고 설명하고 있다. |
||
 |
|
|
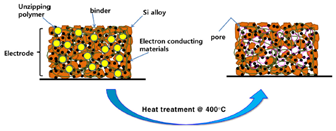
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the porous electrode fabrication process using polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) |
|
 |
 |
|
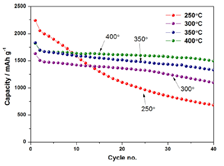
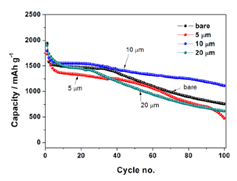
Figure 2. (Left) Cyclic performance of silicon (Si) alloy electrodes at various curing temperatures and (Right) Electrochemical test results; |
|
 |
|
|
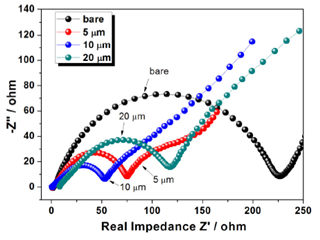
Figure 3. Nyquist plots of firstcharge electrode (measured in the frequency range 0.01–100 kHz) |
|
- Title: A pore-structured Si alloy anode using an unzipping polymer for a lithium ion battery - 한국전기연구원 연구팀은 binder로 사용되는 PAI (Polyamideimide)를 섭씨 400도의 온도에서 curing하여 imidization한 PI (Polyimide)와 PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate)의 unzipping을 이용해 집전제와의 접착력이 우수하고 극판 내부에 많은 기공을 포함한 다공성 구조의 극판을 만드는 방법을 제시하였다. (Figure 1) - PAI의 구조와 특성을 유지하면서 curing하는 온도는 섭씨 350도까지로 알려져있고, 그 이상의 온도에서 curing시 경도는 향상되나 접착력은 감소하는 것으로 알려져있다. 그러나 이번 연구결과에서 섭씨 400도에서 curing시 집전제와의 접착력, 특히 midpoint에서의 접착력은 증가하여 전지성능의 향상을 가져온 것으로 설명하고 있다. 장기 사이클 테스트 결과 초기용량 1821mAh/g이고 40cycle에서 약 1500mAh/g의 용량을 보여 82.4%의 용량유지율을 보여주었다.(Figure 2) - PI binber만으로는 극판의 팽창 문제를 해결할 수 없었다. 그래서 섭씨 400도에서 PMMA의 unzipping을 통한 극판 내부에 공극을 형성함으로써 해결했다고 보고하고 있다. 특히 평균입도 10um의 PMMA 사용시 초기 cycle 용량유지율 (87.6%), 100cycle에서의 용량유지율 (61.8%)에서 가장 우수한 성능을 보여주었다. 극판 팽창 측면에 있어서는 평균입도 20um의 PMMA사용시 가장 뛰어난 특성을 보여주었으나 전지특성의 큰 저하가 발생하였는데 EIS (Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy) 결과 pore size 10um까지는 ~1.6 Ohm으로 저항이 감소하지만 20um pore size에서는 오히려 8.09 Ohm으로 증가함을 보여줌으로써 극판 내부의 공극률과 전지특성과의 관계를 설명하고 있다.(Figure 3) 자료출처: Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 47, 1127–1136 (2017) |
|

