| WPM 고성능 이차전지소재 사업단 소식지 | 2016.08 |
기술정보
[동아대학교] Glue-Nanofiller를 사용하여 이방성으로 지향된 grain 사이의 계면 결합을 향상시킨 양극 활물질
 |
 |
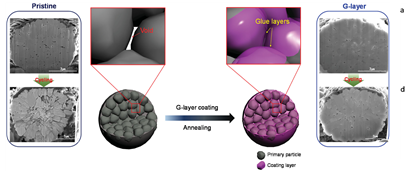
| Figure 1. The scheme shows a formation of glue-layer (purple) in a NCA secondary particle (gray) during the coating processes. | Figure 2. Photographs and SEM images of pristine and G-layer powders after pellet density test. |
 |
|
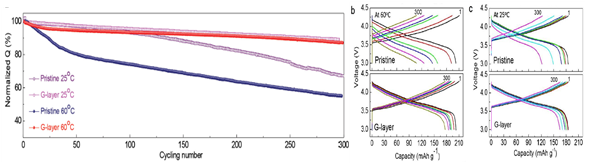
| Figure 3. a) Cycle performance of the pristine and G-layer samples between 3.0-4.3V. b) cycling at high temperature (60℃) c) cycling at room temperature (25℃) | |
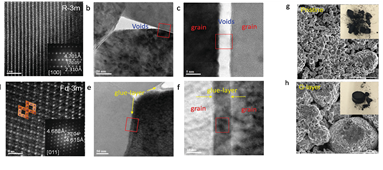
- Title : Enhancing Interfacial Bonding between Anisotropically Oriented Grains Using a Glue-Nanofiller for Advanced Li-Ion Battery Cathode (Advanced Materials Volume 28, Issue 23, (2016) 4705-4712) - UNIST의 조재필 교수진그룹은 spinel-like의 LixCoO2 (MT-LCO,x<1)를 이용한 glue- nanofiller (G-layer) 개념을 도입하여 1차 입자 사이의 void volume을 채우고, 2차 입자 외부 코팅층을 형성하여 전기화학적 특성을 향상시키는 방법을 Advanced Materials에 발표하였다. - Spinel-like 구조 형성 및 잔존리튬과의 반응성을 고려하여 600℃에서 반응시킨 MT-LCO는 이방성으로 지향된 grain 사이의 void volume을 채움으로써 2차 입자의 기계적 강도를 향상시키고, spinel 구조가 가지는 8a, 16d의 추가적인 lithium site에 잔존리튬을 accomodate 할 가능성을 염두에 두고 개발하였다. - G-layer 도입을 통해 Ni-rich 층상계 물질이 가지는 고온 환경에서의 전기화학 성능열화를 개선하는 결과를 얻었으며, NCA의 경우, 25℃와 60℃ 조건에서 방전용량을 normalize했을 때 수명진행에 따라 방전용량의 차이가 없는 결과를 확인하였다. |
|
[서울대학교] High rate charging induced intermediate phase for LIB x-layered materials
 |
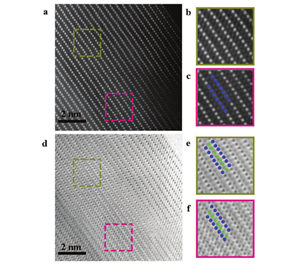 |
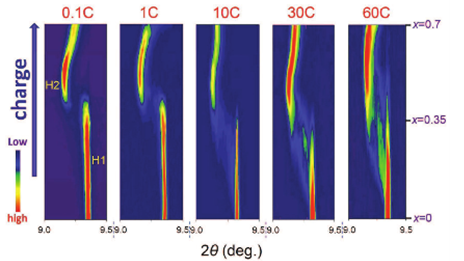
| Figure 1. In situ | Figure 2. Structure |
- Title: High-rate charging induced intermediate phases and structural changes of x-layered-structured cathode for lithium-ion batteries 미국의 Brookhaven National Laboratory 에 Xiao-Qing Yang 그룹은 빠르게 충전하는 방식으로 in situ XRD와 HAADF 및 ABF를 통해서 Li-ion battery의 양극 소재인 NCM111 의 intermediate phases를 확인하였다고 Advanced Energy Materials에 발표하였다. - 배터리 양극소재로 주로 쓰이고있는 NCM 물질의 경우 solid solution reaction을 하는 것으로 알려져있다. 하지만 in-situ XRD와 STEM 분석을 통해서 빠른 충전시에 NCM 물질도 non-equlibrium phase transition behavior를 나타내는 것을 확인하였다. 10C rate 이상에서 in-situ XRD에서 H1-H2 two phase reaction 구간에서 intermediate phase peak을 관찰할 수 있었으며 STEM-HAADF와 ABF를 통해 Phase coexistence heterogeneities와 Li-poor phase에 생기는 Li이 tetrahedral site에 trapped 되어있는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. - 이번 연구를 통해서 빠른 충전에서 intermediate phase를 만든다고 최근에 보고 된 olivine 물질인 LFP 뿐 아니라 x-layered structure를 가지는 양극소재 NCM에서도 빠른 충전시 intermediate phase를 만들 수 있음을 확인하였다. 결과적으로 다양한 종류의 양극소재 물질에서 intermediate phase를 생성함을 확인할 수 있었으며, 이를 통해 빠른 충전에서의 메커니즘을 찾는 이론적 및 실험적인 연구를 더욱 진보시킬 수 있을 것으로 예상된다. (Advanced Energy Materials , 2016) |
|
[성균관대학교] In situ analyses for ion storage materials 배터리 작동 중 이온 저장 소재의 실시간 분석
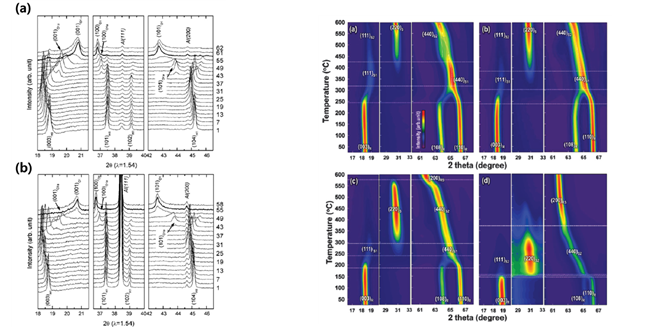 |
| Fig. 6 In situ XRD patterns of (a) the uncoated LiCoO2 and (b) the ZrO2 coated LiCoO2 collected during the 1st charge to 4.8 V at C/4.5 rate in the (003) to (104) region. (Reproduced from ref. 25 with permission from the Electrochemical Society, 2006) Fig. 9 Contour plots of the time-resolved XRD patterns at the selected 2thera range for the charged (a) NMC433, (b) NMC532, (c) NMC622 and (d) NMC811. (Reproduced from ref. 32 with permission from the American Chemical Society, 2014 |
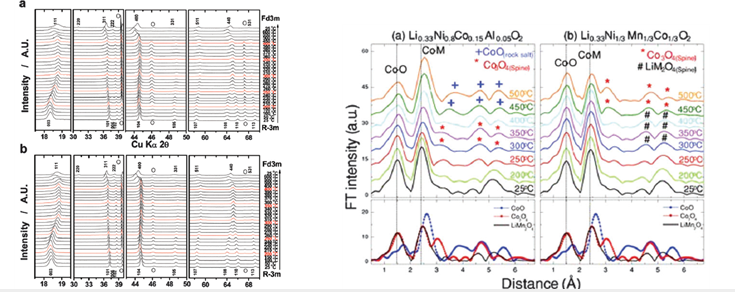 |
| Fig. 11 In situ high-temperature (HT) XRD patterns of the (a) uncoatedand (b) AlF3-coated Li0.35[Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3]O2 after chemical delithiation in temperature range of 25–600 ℃. (Reproduced from ref. 38 with permission from the American Chemical Society, 2010). Fig. 43 Comparison of the Co EXAFS spectra of the overcharged (a) Li0.33Ni0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 and (b) Li0.33Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 electrodes with reference oxides spectra (bottom panel) during heating up to 500 ℃. (Reproduced from ref. 27 with permission fromWiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2013). |
- Title: In situ analyses for ion storage materials - Development of high performance electrode materials for energy storage is one of the most important issues for our future society. However, a lack of clear analytical views limits critical understanding of electrode materials. This review covers useful analytical work using X-ray diffraction, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, microscopy and neutron diffraction for ion storage systems. The in situ observation facilitates comprehending real-time ion storage behaviour while the ion storage system is operating, which help us to understand detailed physical and chemical properties. - 소재 개발에 있어 소재들의 작동 원리 및 퇴화 메커니즘을 먼저 이해해야 이를 바탕으로 소재의 개발 및 개선이 가능하기 때문에 “이온 저장 시스템을 대표하는 리튬이온전지용 전극 소재를 실시간으로 분석할 수 있는 고급분석 방법“에 대해 강조함. - 배터리가 작동하는 동안 실시간 분석을 통해 전극 소재의 작동 원리, 퇴화 원인 규명의 심도 있는 분석 진행. - 분석할 때 분석 관점을 구체적으로 제시함으로써 다른 연구자들이 전극 소재를 개발할 때 기존의 결점을 보완하는 방향으로 디자인할 수 있도록 방향을 제시함. - 위와 같은 내용들을 인용지수(IF) 34.09 에 해당하는 세계 최고 권위 화학誌에 배터리 작동 중 이온 저장 소재의 실시간 분석에 관한 리뷰(Review) 논문을 게재함. (Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, Advance Article, First published online 21 Jul 2016) |
[포항공과대학교] ToF-SIMS를 이용한 Silicon의 Li insertion mechanism 규명
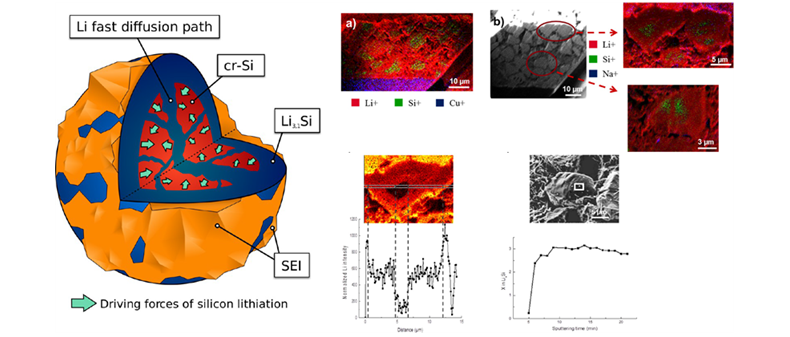 |
- Title :Multiscale Investigation of Silicon Anode Li Insertion Mechanisms by Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometer Imaging Performed on an In Situ Focused Ion Beam Cross Section - Grenble Alpes Univ.와 CNRS-Chimie ParisTech는 ToF-SIMS를 이용하여 Si의 Li insertion mechanism을 관찰하여 Chemistry of Materials에 발표하였다. - 기존의 TEM, AES 등을 이용한 분석은 이루어졌지만 Core shell model에 대한 관찰은 어려웠다. 이번 연구에서 FIB와 ToF-SIMS를 이용하여 이를 규명하였다. - 이를 통해 Crystal Si를 초기 충전 과정에서는 표면부터 Li이 Insertion될 뿐만 아니라 입자 내에 존재하는 Subgrain boundary를 통해 Li diffusion이 쉽게 발생하여 Insertion이 내부에도 특정 길을 통해 발생할 수 있는 것을 확인하였다. - 또한, 이러한 현상은 전극 표면으로부터 거리에 관계없이 모든 입자에서 동일하게 발생하는 것을 관찰하였다. 그리고 Si이 충분히 많은 충방전을 거친 뒤 모두 비정질로 상전이가 일어난 뒤에는 균일한 Li insertion이 발생하였다. (Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1566−.1573) |
본 메일은 발신전용입니다. 문의사항은 eunmi.kang@samsung.com으로 문의하십시오.
COPYRIGHT(C) 2013. SAMSUNG SDI INC. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.